
Different Types of UV Exposure: Understanding the Sun’s Effects on Our Skin
Introduction
As summer approaches and we spend more time outdoors, it’s important to understand the different types of UV exposure and their effects on our skin. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, emitted by the sun, is invisible to the naked eye but can have significant impacts on our health. In this blog, we will delve into the three main types of UV radiation—UVA, UVB, and UVC—and explore the various ways they affect our skin.
1. UVA Radiation
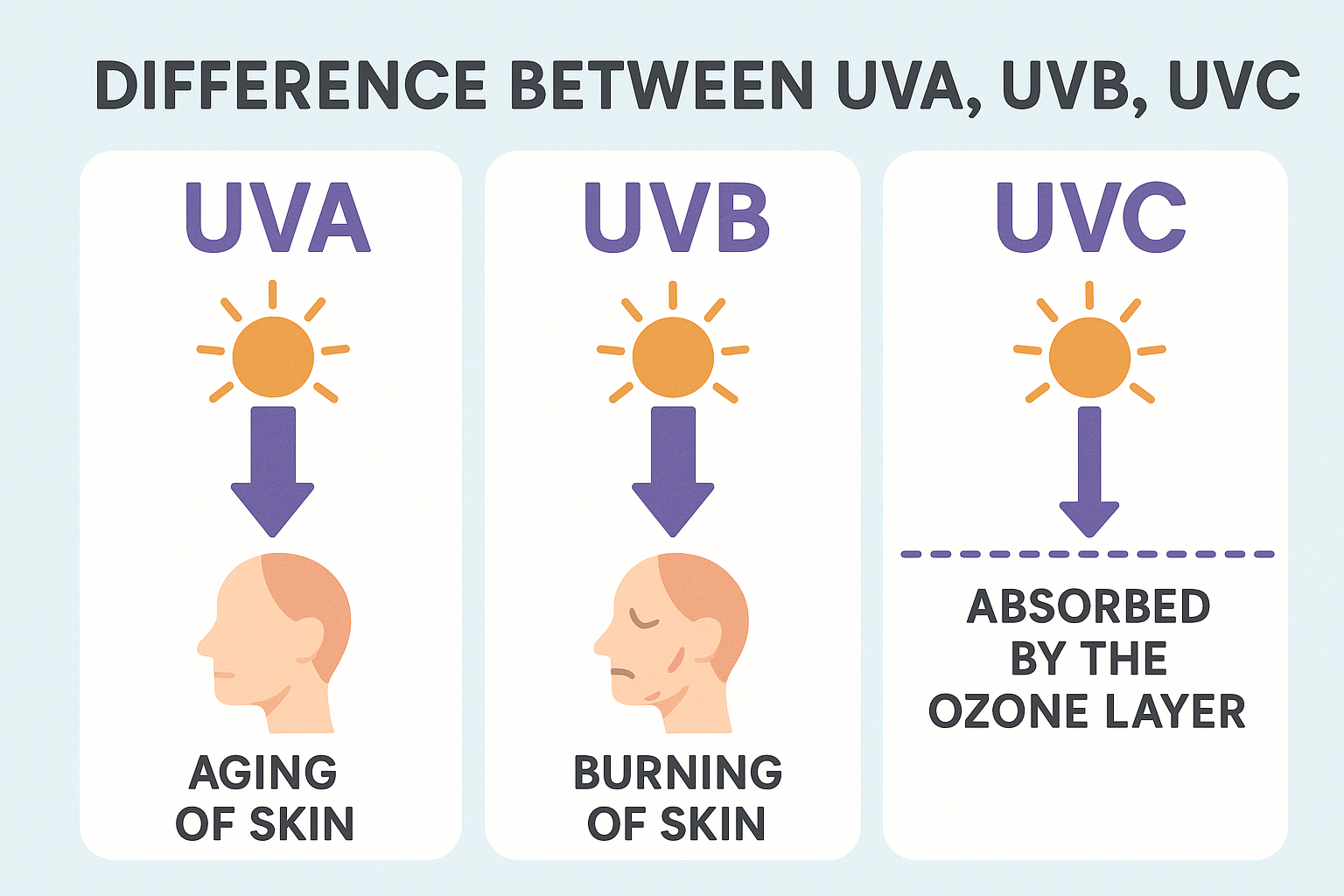
UVA radiation, also known as long-wave radiation, accounts for the majority of UV radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. It can penetrate deep into the skin, reaching the underlying layers, and is present at relatively consistent levels throughout the day and year. UVA rays are responsible for immediate tanning and are often associated with skin aging and wrinkling. Additionally, UVA exposure can suppress the immune system, making the skin more susceptible to damage and increasing the risk of skin cancer.
2. UVB Radiation
UVB radiation, or medium-wave radiation, is responsible for most sunburns. It has a shorter wavelength than UVA and is partially absorbed by the Earth’s ozone layer. UVB rays are strongest during midday and summer months, and their intensity varies based on geographic location and time of year. Overexposure to UVB radiation can lead to long-term skin damage, including premature aging, sunspots, and an increased risk of skin cancer.
3. UVC Radiation
Unlike UVA and UVB radiation, UVC radiation has the shortest wavelength and is almost entirely absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere, particularly the ozone layer. However, it is important to note that UVC rays can be generated artificially, such as in certain industrial processes and some medical equipment. UVC radiation is highly dangerous and can cause severe skin burns, eye damage, and other health issues. Thankfully, natural UVC radiation from the sun is not a significant concern for human health.
4. The Impact of UV Exposure on the Skin
a. Sunburn
One of the most common consequences of excessive UV exposure is sunburn. Sunburn occurs when the skin’s DNA is damaged by UV radiation, triggering an inflammatory response. Symptoms include redness, pain, swelling, and blistering. Severe sunburns can cause fever, chills, and even lead to dehydration and infection. Sunburn increases the risk of skin cancer, particularly melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
b. Premature Aging
Repeated exposure to UV radiation can lead to premature aging of the skin. UVA rays penetrate the skin deeply, damaging collagen and elastin fibers, which results in sagging, wrinkling, and the loss of elasticity. UVB rays can also contribute to premature aging by damaging the skin’s outer layers. Protecting the skin from UV radiation can help slow down the aging process and maintain a youthful appearance.
c. Skin Cancer
UV radiation is a known carcinogen and a leading cause of skin cancer. Prolonged exposure to UVA and UVB rays increases the risk of developing various types of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. It is estimated that one in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. Regular use of sun protection measures and avoiding excessive sun exposure are crucial in reducing this risk.
5. Protection Against UV Exposure
Protecting Your Skin: Effective Measures Against UV Exposure
Introduction
With the increasing awareness of the harmful effects of UV radiation on our skin, it’s crucial to take proactive steps to protect ourselves. Whether you’re planning a day at the beach or simply stepping outside, safeguarding your skin from UV exposure should be a top priority. In this blog, we will explore effective measures and strategies to shield your skin from the damaging effects of the sun’s UV radiation.
1. Seek Shade
One of the simplest and most effective ways to minimize UV exposure is to seek shade when the sun is at its strongest. The sun’s rays are most intense between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., so try to stay indoors or find shelter under a tree, umbrella, or awning during these peak hours. By reducing direct exposure to the sun, you can significantly lower the risk of sunburn and other skin damage.
2. Wear Protective Clothing
Clothing can act as a physical barrier between your skin and harmful UV rays. When spending time outdoors, opt for tightly woven, lightweight clothing that covers as much skin as possible. Long-sleeved shirts, pants, and skirts made of sun-protective fabrics offer excellent defense against UV radiation. Additionally, wide-brimmed hats can shield your face, neck, and ears, while UV-blocking sunglasses protect your eyes and the delicate skin around them.
3. Apply Sunscreen Daily
Sunscreen is a crucial component of any sun protection regimen. When selecting a sunscreen, choose one with a broad-spectrum formula that provides protection against both UVA and UVB rays. Look for a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 or higher and apply it generously to all exposed skin, including your face, neck, ears, and hands. Remember to reapply every two hours, or more frequently if you’re swimming or sweating.
4. Use UV-Protective Umbrellas and Sunshades
If you’re planning a beach trip or spending an extended period outdoors, consider investing in a UV-protective umbrella or sunshade. These portable accessories provide additional shade and create a barrier between you and the sun’s rays. Look for umbrellas with a high UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) rating to ensure maximum protection.
5. Be Mindful of Reflective Surfaces
UV radiation can bounce off reflective surfaces, such as water, sand, snow, and concrete, intensifying your exposure. Keep this in mind when planning outdoor activities and take extra precautions in these environments. Apply sunscreen more frequently, wear protective clothing, and consider using a wide-brimmed hat and UV-blocking sunglasses to mitigate the effects of reflected UV radiation.
6. Check the UV Index
The UV Index is a helpful tool that indicates the intensity of UV radiation in your area on a given day. Before heading out, check the UV Index forecast and plan accordingly. If the index is high, take extra precautions to protect your skin. Seek shade, wear protective clothing, and apply sunscreen liberally to minimize your risk of sunburn and other UV-related skin damage.
7. Don’t Forget Your Lips and Ears
Often overlooked, the lips and ears are highly susceptible to sunburn. Make sure to apply a lip balm with SPF 30 or higher to protect your lips from UV radiation. Additionally, apply sunscreen to your ears or wear a wide-brimmed hat that covers them adequately.
8. Regular Skin Examinations
Performing regular skin examinations allows you to detect any changes or abnormalities early on. Keep an eye out for new moles, changes in the color, shape, or size of existing moles, or any other skin irregularities. If you notice anything unusual, consult a dermatologist promptly. Early detection is key in successfully treating skin cancer







This Post Has 0 Comments