Understanding UV Rays and How They Impact Your Tan
When it comes to tanning and sun exposure, knowing the difference between UV rays matters. The sun gives off UVA, UVB, and UVC radiation—and each one affects your skin differently. From sunburns to aging and skin cancer risks, these rays play a big role in how your skin reacts.
In this post, we’ll break down how each UV type works—and how they connect to tanning methods like those available at Trutan.net or when using Melanotan responsibly for safer, more effective results.
What Are UVA, UVB, and UVC Rays? Let’s Break It Down
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a form of energy from the sun, with wavelengths shorter than visible light but longer than X-rays. It’s grouped into three types—UVA, UVB, and UVC—each affecting your skin in different ways.
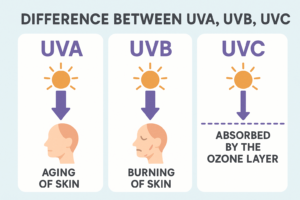
- UVA (Ultraviolet A)
• Wavelength: 320–400 nm
• Penetration: Reaches deep into the dermis
• Effects: Causes early aging, wrinkles, long-term skin damage
• Tanning: Triggers quick tanning, not burning
• Protection: Blocked by broad-spectrum sunscreens
UVA makes up around 95% of UV rays reaching Earth. It can get through clouds and glass, so protection is key—even on overcast days.
- UVB (Ultraviolet B)
• Wavelength: 280–320 nm
• Penetration: Affects the skin’s top layer (epidermis)
• Effects: Causes sunburn, cell damage, and increases cancer risk
• Tanning: Helps boost melanin for delayed tanning
• Protection: SPF ratings measure UVB shielding
UVB is stronger than UVA and is the main cause of sunburn. It’s most intense from 10 AM to 4 PM, and varies with season and location.
- UVC (Ultraviolet C)
• Wavelength: 100–280 nm
• Penetration: Blocked by the ozone—doesn’t reach Earth
• Effects: Harmful from artificial sources (e.g. UV lamps)
• Tanning: Not linked to tanning at all
UVC is the most dangerous type of UV radiation—but natural sunlight won’t expose you to it. Still, some industrial equipment may emit UVC, so caution is advised in controlled settings.
Tanning and UV Safety – Smarter Ways to Get That Glow
Tanning is a popular way to boost confidence and enhance your look—but traditional methods like sunbathing and sunbeds come with risks from UVA and UVB exposure.
Trutan.net: A Sunless Tanning Alternative
At Trutan, you’ll find safe tanning solutions like Melanotan II—a peptide that helps trigger melanin production without long hours in the sun. It’s a smarter, low-UV way to build your tan and protect your skin.
Explore safe, effective tanning options now at Trutan.net.
Using Melanotan – What to Know Before You Start
Melanotan is a synthetic version of the body’s natural tanning hormone (MSH). When used correctly, it can:
• Help build a tan with less sun exposure
• Lower your chances of sunburn through added melanin
• Support a deeper, longer-lasting glow
That said, it’s important to use it wisely:
• Always buy from a trusted source like Trutan.net
• Be aware of possible side effects—like nausea, pigmentation shifts, or increased libido
• Speak with a healthcare provider first if you have skin concerns or health conditions
Final Thoughts – Smarter Sun Habits Start Here
Knowing the difference between UVA, UVB, and UVC rays helps you make better choices for your skin. Whether you’re going for a natural glow or using a peptide like Melanotan, the goal is the same—protect your skin while getting the look you love.
Keep these tips in mind:
• Use broad-spectrum SPF daily
• Wear sunglasses and sun-safe clothing
• Skip sun exposure during peak hours
• Try safer tanning options like those at Trutan.net
Tanning & UV Rays – What to Know Before You Glow
When it comes to sun exposure, it helps to understand the types of UV rays—and how they affect your skin. Pairing smart skincare with informed tanning choices helps you glow safely and protect your skin long term.
Here’s how TruTan products relate to each UV type:
🌞 UVA (Aging Rays)
• Penetrates deep, causing wrinkles and early aging
• Some TruTan products support UVA care, especially full-spectrum skincare lines
🔥 UVB (Burning Rays)
• Causes sunburn and helps make vitamin D
• TruTan accelerators support natural tanning but don’t protect—add SPF!
🚫 UVC (Blocked Rays)
• Doesn’t reach Earth naturally
• No need for UVC protection in TruTan products
⚠️ Reminder:
TruTan enhances tanning—it’s not a sunscreen. Always use SPF with any UV exposure.
